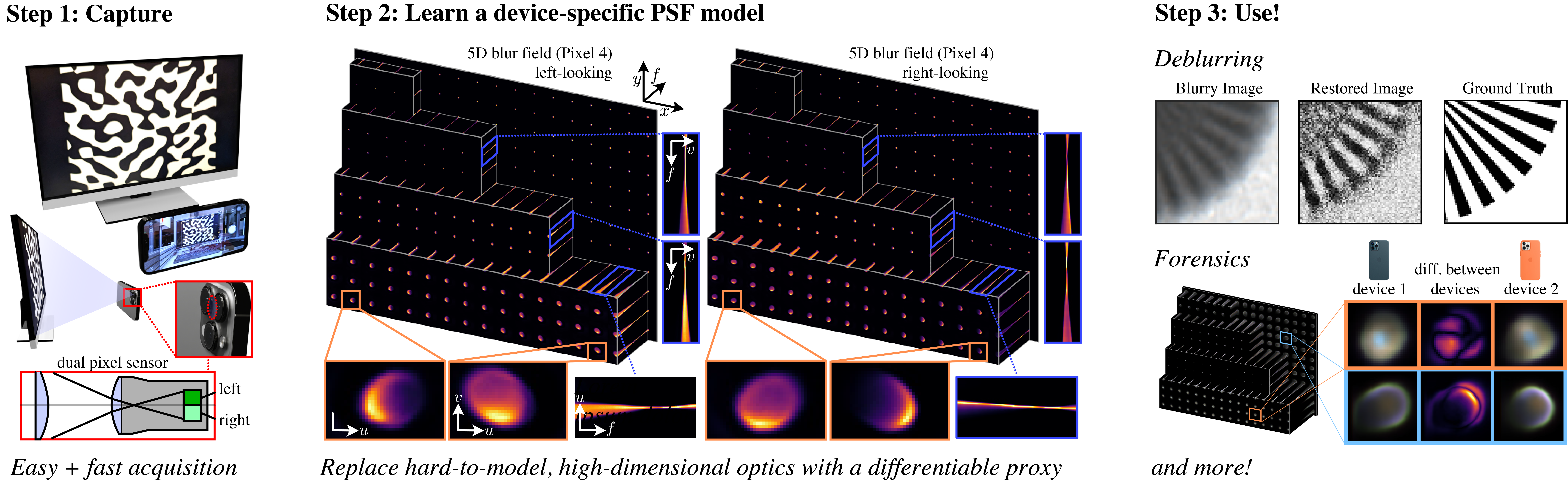
Abstract
Optical blur is an inherent property of any lens system and is challenging to model in modern cameras because of their complex optical elements. To tackle this challenge, we introduce a high‑dimensional neural representation of blur—the lens blur field—and a practical method for acquisition.
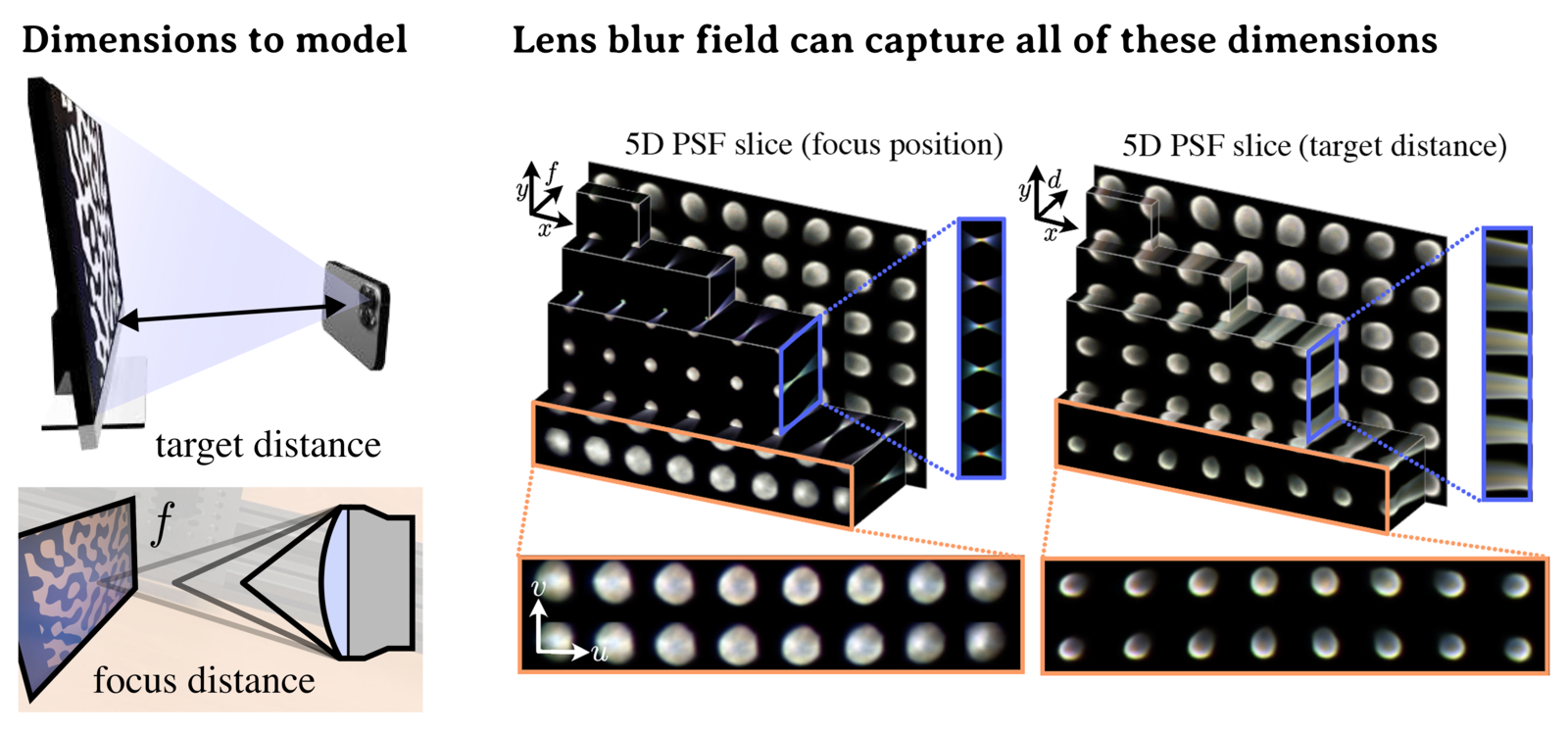
The lens blur field is a multilayer perceptron (MLP) designed to (1) accurately capture variations of the lens 2‑D point spread function over image‑plane location, focus setting, and optionally depth; and (2) represent these variations parametrically as a single, sensor‑specific function. The representation models the combined effects of defocus, diffraction, aberration, and accounts for sensor features such as pixel color filters and pixel‑specific micro‑lenses.
We provide a first‑of‑its‑kind dataset of 5‑D blur fields—for smartphone cameras, camera bodies equipped with a variety of lenses, etc. Finally, we show that acquired 5‑D blur fields are expressive and accurate enough to reveal, for the first time, differences in optical behavior of smartphone devices of the same make and model.
Overview
Optical blur, or point spread function (PSF) is an umbrella term for a laundry list of image degrading effects such as defocus, diffraction, and aberrations. It's hard to calibrate because it varies with sensor position, focus, target distance, and where you look on the image plane. We introduce Lens Blur Fields: tiny MLPs that can model this high-dimensional PSF.
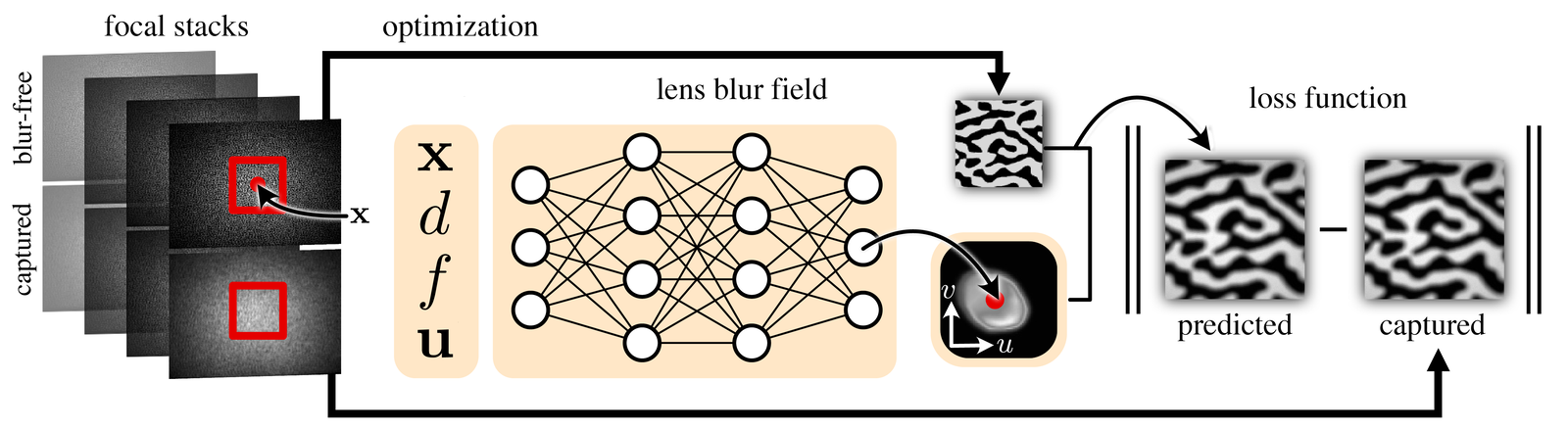
Our capture setup only needs a monitor + a simple phone/camera stand. The pipeline is light:
- Capture focal stacks of monitor patterns (in just minutes!)
- Solve a non-blind deconvolution to train the MLP
- Get a continuous, device-specific PSF model
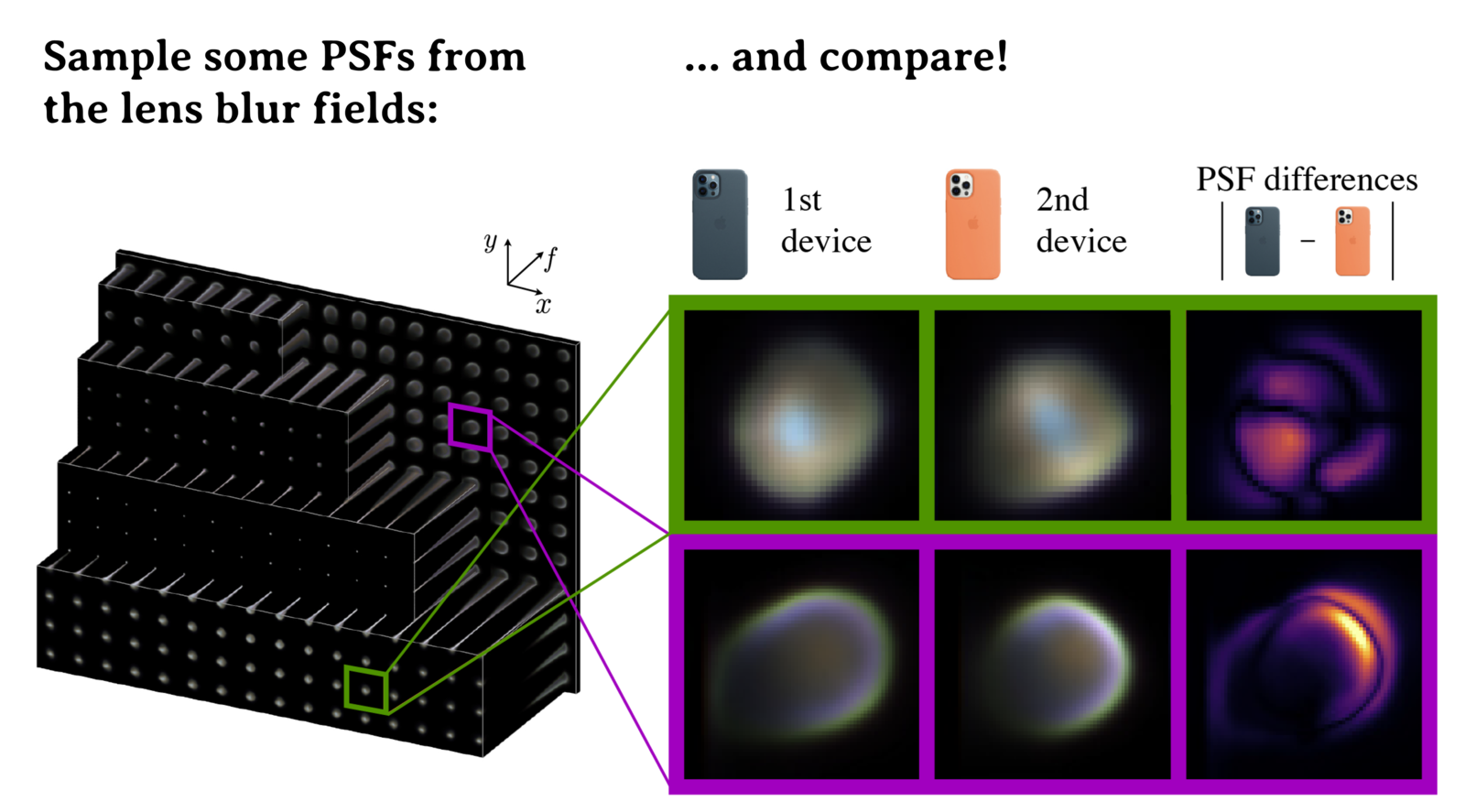
Applications
Two smartphones of the same make can have subtly different PSFs. We show this with the lens blur fields of two iPhone 12 Pros:
Lens blur fields let you render device-specific depth-of-field, blur a resolution chart or a 3D scene.

And with more realistic renders, we can also do better device-specific image restoration.
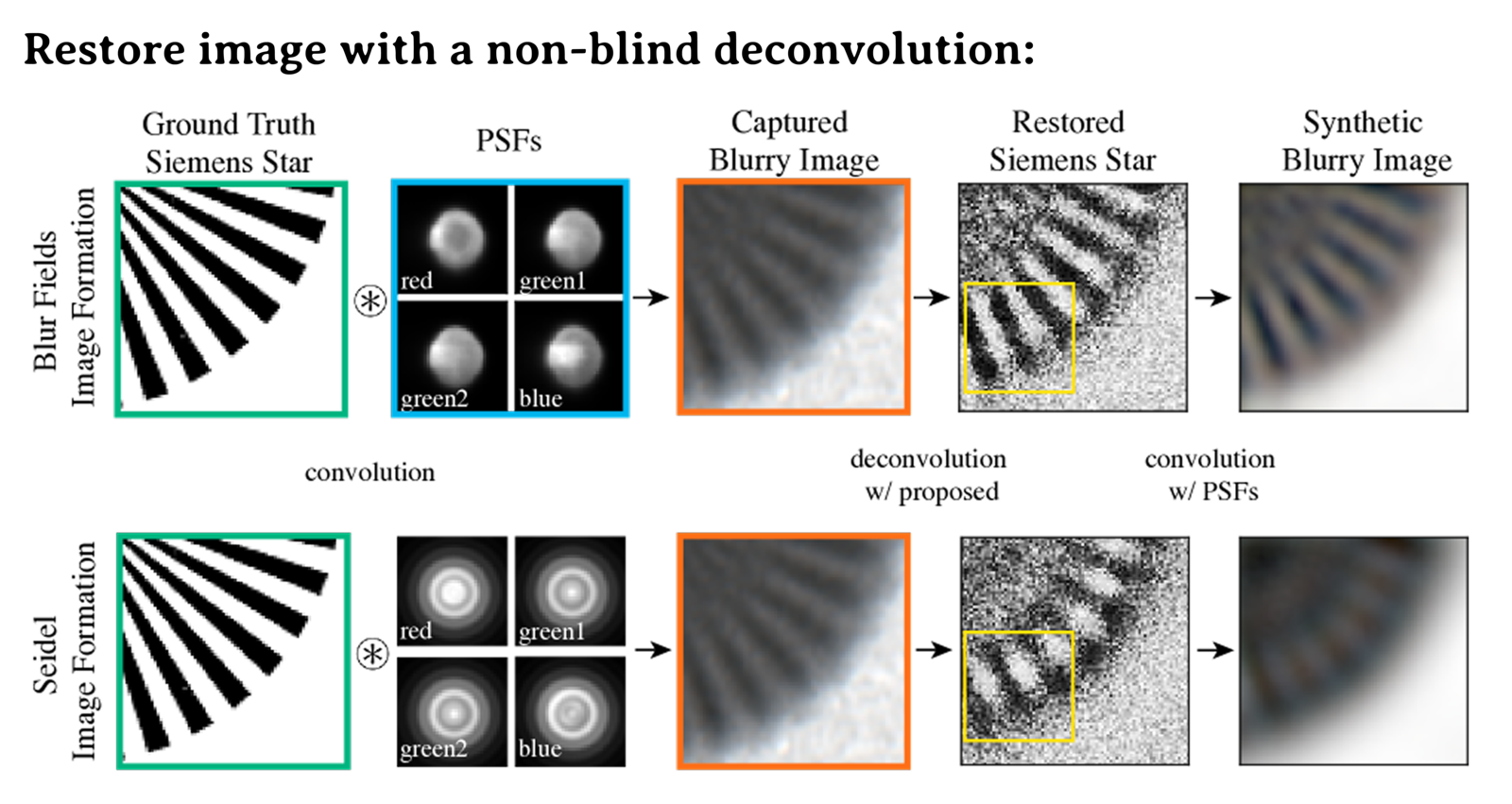
Dataset
We'll be releasing the first dataset of 5D and 6D lens blur fields for smartphone & SLR lenses, plus captures used for training. Stay tuned!

BibTeX
@article{lin2025learning,
title={Learning Lens Blur Fields},
ISSN={1939-3539},
url={http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2025.3578587},
DOI={10.1109/tpami.2025.3578587},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence},
publisher={Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)},
author={Lin, Esther Y. H. and Wang, Zhecheng and Lin, Rebecca and Miau, Daniel and Kainz, Florian and Chen, Jiawen and Zhang, Xuaner and Lindell, David B. and Kutulakos, Kiriakos N.},
year={2025},
pages={1–12}}